A satellite is an object that orbits around a larger celestial body, such as a planet or a moon. In the context of space technology, a satellite refers to an artificial object that is intentionally placed into orbit around the Earth. Satellites serve various purposes, including communication, weather monitoring, scientific research, navigation, and surveillance.
Table of Contents
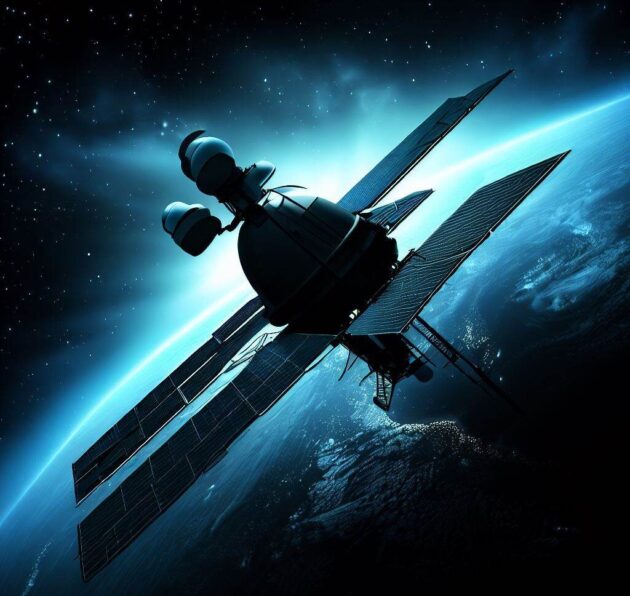

Satellites are composed of several key parts, each playing a specific role in their functionality. Here are the main components of a satellite:
Outer Structure: The outer structure of a satellite is typically a cylindrical or box-like shape. It provides protection to the internal components from the harsh conditions of space, such as extreme temperatures, radiation, micrometeoroids, and vacuum. decay of isotopes into electricity

Power System: Satellites require a power source to operate their systems. They typically use solar panels to convert sunlight into electricity. The solar panels are usually mounted on the satellite’s body and generate electricity to charge onboard batteries. In some cases, satellites may also use radioisotope thermoelectric generators (RTGs) that convert the heat generated by the radioactive.
Antennas: Satellites use antennas to transmit and receive signals. They can be designed for various purposes, such as communication antennas for relaying signals between ground stations or user devices, or scientific antennas for collecting data from the environment.

Payload: The payload refers to the primary equipment or instruments carried by a satellite to perform its intended mission. For communication satellites, the payload consists of transponders that receive signals from the ground and retransmit them to another location, enabling communication over large distances. Weather satellites have payloads that include cameras and sensors to observe and gather data about. Earth’s atmosphere and weather patterns

Communication Subsystem: This subsystem includes the components responsible for transmitting and receiving signals to and from Earth. It consists of modems, transponders, amplifiers, and other necessary equipment for signal processing, encoding, decoding, and relaying.

Control and Attitude Determination System: Satellites need systems to control their orientation and movements in space. This includes attitude determination sensors (such as gyroscopes, magnetometers, and sun sensors) to determine the satellite’s position and attitude, as well as thrusters or reaction wheels to adjust its orientation and maintain stability.
Onboard Computers: Satellites are equipped with onboard computers that control their operations, process data, execute commands, and manage various subsystems. These computers are programmed with specialized software to handle the specific tasks of the satellite.
Thermal Control System: Satellites operate in extreme temperature variations, from extreme cold in shadowed areas to intense heat when exposed to the Sun. The thermal control system consists of insulation, heat sinks, radiators, and heaters to regulate and maintain the temperature within the satellite’s operational limits.
Telemetry, Tracking, and Command Systems (TT&C): These systems allow ground operators to communicate with and monitor the satellite. TT&C systems enable the transmission of commands to the satellite, reception of telemetry data (such as status information, sensor readings, and health diagnostics), and tracking the satellite’s position and orbit.

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What are the main parts of a satellite?
A satellite typically consists of key components such as the payload, power system, communication system, propulsion system, attitude control system, thermal control system, and structural frame.
2. What is the function of the payload in a satellite?
The payload is the main working part of a satellite, which varies depending on its mission. For example, a communication satellite’s payload includes transponders, while an Earth observation satellite carries cameras and sensors.
3. How do satellites generate power?
Most satellites use solar panels to generate electricity, which is stored in onboard batteries to power the satellite when it’s in the Earth’s shadow.
4. What is the role of the communication system in a satellite?
The communication system consists of antennas and transponders that help send and receive signals, allowing satellites to transmit data, television broadcasts, or internet services to Earth.
5. How do satellites maintain their position in space?
Satellites use an attitude control system (ACS), which includes gyroscopes, reaction wheels, and thrusters to stabilize and adjust their orientation in space.
6. Why do satellites need a propulsion system?
A propulsion system, often using chemical or electric thrusters, helps satellites adjust their orbit, maintain position, and sometimes deorbit at the end of their mission.
7. How do satellites handle extreme temperatures in space?
Satellites use a thermal control system, which includes heat shields, radiators, and insulation materials to protect them from extreme heat and cold in space.
8. What materials are used to build satellites?
Satellites are made of lightweight, durable materials such as aluminum, titanium, and carbon composites, which can withstand harsh space conditions.
9. How do satellites communicate with Earth?
Satellites use radio waves to communicate with ground stations. They transmit signals carrying data, which are received and processed on Earth.
10. What happens when a satellite completes its mission?
When a satellite reaches the end of its life, it either:
- Moves to a graveyard orbit (for geostationary satellites)
- Deorbits and burns up in the atmosphere
- Falls into the ocean in a controlled re-entry (if large enough)
AI in Space or Parts of satellite
11. What role does AI play in satellite communication systems?
AI helps optimize data transmission, reduce signal interference, and improve decision-making in real-time for efficient satellite communication.
12. How does AI enhance the satellite’s onboard computer (OBC)?
AI enables smart decision-making, fault detection, and autonomous control in the OBC, reducing dependency on ground control.
13. Can AI improve satellite power systems like solar panels?
Yes! AI algorithms predict power consumption and optimize solar panel positioning for maximum energy efficiency.
14. Is AI used in satellite payload management?
Absolutely. AI manages sensors and instruments, prioritizing data collection based on mission goals and environmental conditions.
15. What is the impact of AI on satellite navigation systems?
AI refines orbital predictions, adjusts positioning, and ensures precise satellite maneuvering even in space debris conditions.
16. How does AI help satellite antennas function better?
AI helps antennas adapt to changing communication demands by steering beams, auto-tracking, and enhancing signal clarity.
17. Can AI improve satellite thermal control systems?
Yes, AI predicts temperature fluctuations and adjusts heaters or radiators to maintain optimal internal temperatures.
18. How does AI assist in attitude control systems (ACS)?
AI helps stabilize the satellite, adjusting orientation based on mission needs using gyros and reaction wheels efficiently.
19. What’s the AI role in satellite imaging systems?
AI enhances image quality, auto-detects objects, and compresses data for faster transmission to Earth.
20. Can AI help satellites avoid collisions in space?
Definitely. AI predicts potential collisions with space debris and calculates safe avoidance maneuvers autonomously.
21. How does AI make satellites more autonomous?
With AI, satellites can monitor their own health, make mission-critical decisions, and adapt to unexpected space conditions without waiting for Earth-based commands.





