Brave browser and Google Chrome stand out as popular web browsers, each providing a distinct blend of performance, privacy, and features.
Table of Contents
In the dynamic landscape of web browsers, users are continuously exploring alternatives that prioritize their privacy and enrich their browsing journeys. Two prominent contenders in this domain are Google Chrome and Brave Browser, each presenting distinctive features and functionalities.
Google Chrome, widely embraced for its intuitive interface and extensive support for extensions, has faced scrutiny due to concerns regarding privacy and data gathering practices. Conversely, Brave Browser distinguishes itself by placing a strong emphasis on user privacy and security, incorporating built-in ad-blocking and tracking prevention mechanisms. It purports to enhance browsing speeds and minimize battery consumption as well.
As browsing habits evolve, it becomes paramount to discern the crucial distinctions between these browsers, empowering users to make well-informed choices and optimize their online interactions. In the subsequent sections, we will explore the fundamental disparities between Brave and Chrome and examine how these disparities might influence your browsing endeavors.
Brave vs Google – Overview
Brave and Google Chrome stand out as popular web browsers, each providing a distinct blend of performance, privacy, and features. Both browsers share the Chromium platform, an open-source project initiated by Google, facilitating the exchange of tools and techniques for enhancement. Brave browser prioritizes privacy and ad-blocking, contrasting Chrome’s emphasis on speed and tight integration with Google services. Visually, both browsers sport clean, user-friendly interfaces for seamless navigation.
Brave’s privacy focus is evident through its built-in ad-blocker and tracking protection, curtailing data collection by websites and advertisers. Additionally, Brave’s desktop and mobile versions refrain from using identifiers, enhancing user privacy. Nonetheless, privacy-conscious users can configure Chrome, Firefox, and Safari for increased privacy, albeit through manual settings adjustments. Regarding performance, both Brave browser and Chrome excel in speed. Brave’s ad-blocking aids faster page-loading, while Chrome’s page preloading feature expedites content access. In terms of features, Chrome boasts a wider array of extensions, while Brave uniquely offers access to cryptocurrencies via the Basic Attention Token (BAT).
Subsequent sections will delve into the specific merits and demerits of each browser, facilitating an informed decision on the optimal choice to align with your preferences.
Is Brave safer than Chrome?
Google represents the quintessence of “Big Tech” corporations and ranks among the most valuable entities globally. Despite its association with the ubiquitous term “googling,” Google primarily operates as an advertising entity. A substantial portion of its considerable annual revenue stems from ad sales.
In facilitating these ads, both the Chrome browser and the Google search engine meticulously gather user data. This data serves as the bedrock for highly personalized advertising endeavors. Essentially, the more insights Google garners about individual users, the greater their profitability through targeted advertisements.
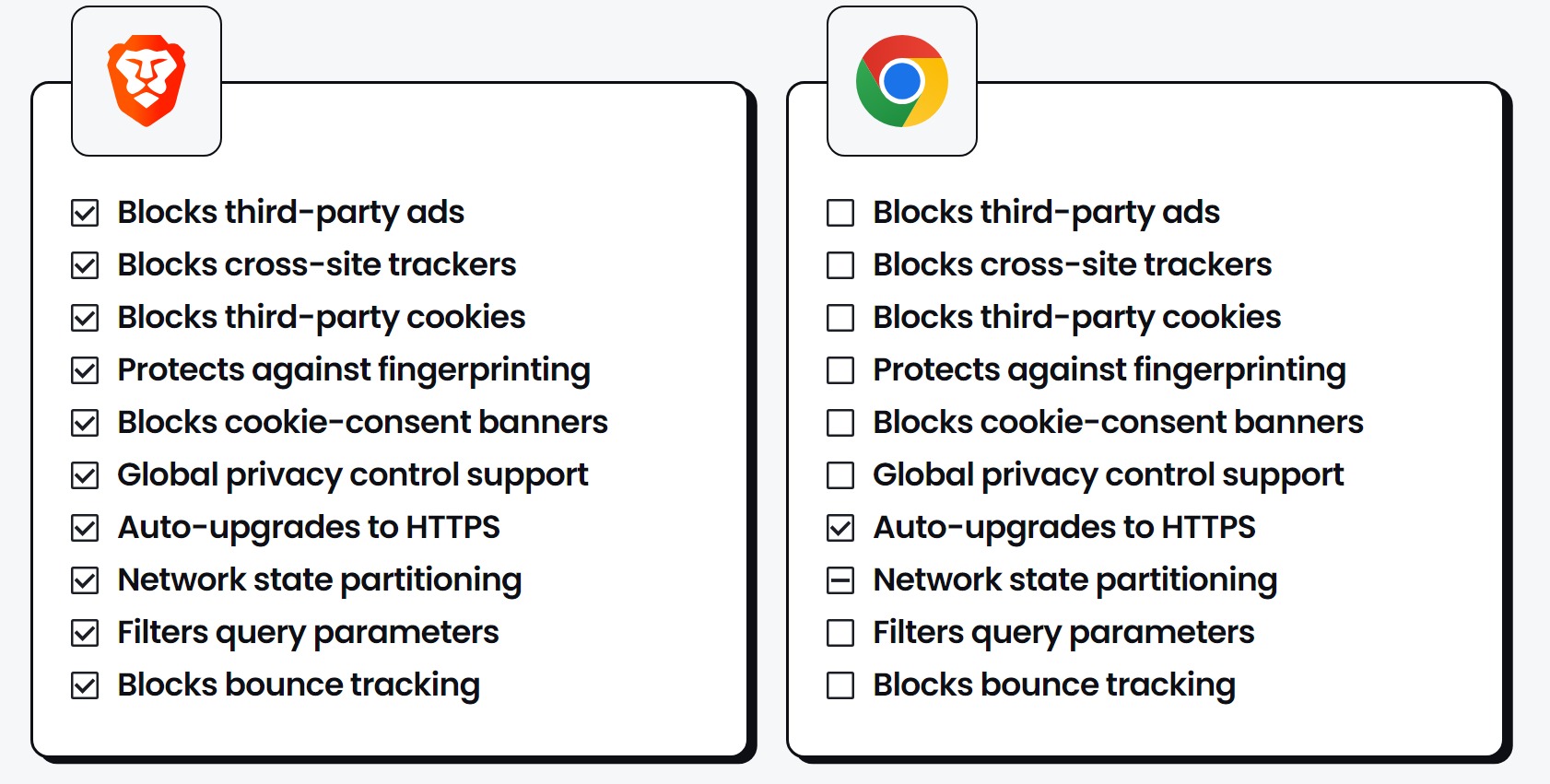
| Privacy Feature | Default Setting |
|---|---|
| Blocks third-party ads | Full Protection |
| Blocks cross-site trackers | Full Protection |
| Blocks third-party cookies | Full Protection |
| Protects against fingerprinting | Full Protection |
| Blocks cookie-consent banners | Full Protection |
| Global privacy control support | Full Protection |
| Auto-upgrades to HTTPS | Full Protection |
| Network state partitioning | Full Protection |
| Filters query parameters | Full Protection |
| Blocks bounce tracking | Full Protection |
The chart above describes the default settings for privacy features, categorized into three levels of protection:
- Full Protection: All privacy features are enabled by default, offering comprehensive protection against various tracking methods.
- Limited Protection: Some privacy features are enabled by default, providing partial protection against tracking.
- No Protection, or Off by Default: Privacy features are not enabled by default, leaving users vulnerable to tracking and data collection.
Chrome, by default, offers limited to no protection against tracking, allowing various forms of tracking such as ads, trackers, cookies, and fingerprinting to operate without user consent.
Does Brave browser have more features than Chrome?
Both Brave and Chrome utilize the open-source Chromium browser engine, which also serves as the foundation for browsers like Edge, Opera, and Vivaldi. This shared foundation ensures that both Brave and Chrome offer a similar user interface and functionality.
Both browsers include fundamental features such as bookmarks and tabs. Additionally, Brave is designed to be compatible with Chrome extensions, meaning that any extension that works in Chrome will also work seamlessly in Brave. However, Brave distinguishes itself by incorporating numerous built-in features, reducing the necessity for additional extensions.
Comparison of Features: Brave vs Chrome
| Feature | Brave | Chrome |
|---|---|---|
| Ad Blocking | ✓ Built-in ad blocker | Chrome Extension Required |
| YouTube Ad Blocking | ✓ YouTube ad blocker | Not Available |
| AI Assistant | ✓ (Not specified) | Not Available |
| Vertical Tabs | ✓ Vertical tabs | Not Available |
| Tab Groups | ✓ Tab groups | ✓ Tab groups |
| Offline Media Playlists | ✓ Offline media playlists | Not Available |
| News & RSS Reader | ✓ News & RSS reader | Not Available |
| Reader Mode | ✓ Reader mode | ✓ Reader mode |
| Night Mode | ✓ Night mode | ✓ Night mode |
| Translations | ✓ Translations | ✓ Translations |
| Cross-device Profile Syncing | ✓ Cross-device profile syncing | Chrome Sync |
| Privacy & Security | ||
| Default Private Search | ✓ Default private search | Not Available |
| Built-in VPN | ✓ Built-in VPN | Not Available |
| Built-in, Private Video Calls | ✓ Built-in, private video calls | Not Available |
| Tor Browsing | ✓ Tor browsing | Not Available |
| Web Torrent Integration | ✓ Web Torrent integration | Not Available |
| Web3 | ||
| Secure, Built-in Wallet | ✓ Secure, built-in wallet | Not Available |
| Crypto Rewards Program | ✓ Crypto rewards program | Not Available |
| IPFS Peer-to-peer File Sharing | ✓ IPFS peer-to-peer file sharing | Not Available |
The comparison table above outlines the availability of various features in Brave and Chrome. Brave offers several built-in features for ad blocking, privacy, security, and Web3 functionality, while Chrome may require extensions or lacks these features entirely.
Chrome vs. Brave: What’s Hot in 2025
Right now, in July 2025, Chrome and Brave are making waves! Chrome just fixed a big security bug, so update it fast to stay safe. Brave is getting super popular, growing 21% this year, because it blocks ads and trackers automatically, keeping your data private. Chrome is crazy fast and works great with Google apps, but some say it tracks too much. Brave feels lighter and has a cool AI helper called Leo. So, do you want speed with Chrome or privacy with Brave?

Search Engine Comparison: Google vs Brave Search
In Chrome, Google serves as the default search engine, aligning with its data collection practices aimed at gathering extensive user data.
Contrastingly, Brave Browser features Brave Search as its default search engine, prioritizing user privacy and security. Brave ensures data protection by refraining from collecting, selling, or compromising user data.
While Google boasts a vast index of pages, Brave Search focuses on quality over quantity. With over 18 billion indexed pages, Brave Search prioritizes relevance, timeliness, and utility in search results. Unlike Google, whose index comprises a significant portion of duplicate content, spam pages, and irrelevant material, Brave Search delivers more precise and valuable search outcomes.
Extension Compatibility and Privacy: Brave vs Chrome
Both Brave and Chrome support Chrome extensions, thanks to their shared Chromium engine. While extensions offer enhanced functionality, they also introduce privacy and security risks. Brave mitigates these risks by integrating robust privacy features, reducing reliance on extensions and ensuring better overall privacy, security, and performance.


